Destiny Formulations
NEURO(X) - Cognitive Performance
NEURO(X) - Cognitive Performance
Couldn't load pickup availability
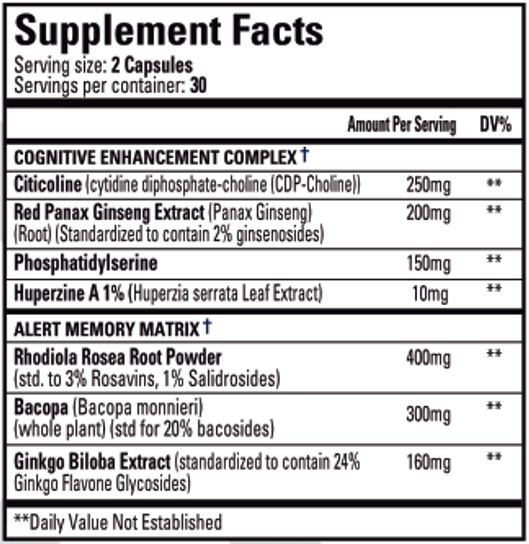
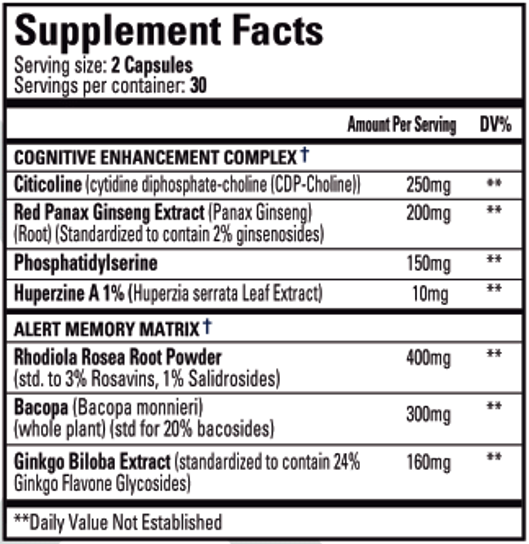
NEURO(X) is a nootropic and adaptogenic dietary supplement that helps support healthy brain function, increases focus and clarity, and enhances memory recall.†
What's Inside?
Performance Breakdown:
- Increased attention & focus ⬆
- Enhances memory recall ⬆
- Prevents cognitive decline ⬇
Mechanism of Action:
- CDP-choline (citicoline) is a nootropic compound with high bioavailability which is readily converted in the brain to the learning neurotransmitter, acetylcholine.
Annotated References:
- This study assessed the potential cognitive-enhancing efects of cticoline as dietary supplement in 60 healthy adult women in a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study.
- The subjects were divided into three experimental groups; a daily oral dose of 250 mg Citicoline, 500 mg citicoline, or placebo for 28 days..
- Evaluation was done by Continuous Performance Test II (CPT-II), a measure sensitive to attentional function..
- The results afyter 28 days showed that individuals on the 250 mg dose of citicoline made fewer omission and commission errors compared to those in the placebo and the 500 mg group! These subjects were able to produce more correct responses on the CPT-II, likely due to improved cognitive inhibition.

E. McGlade, A. Locatelli, J. Hardy, T. Kamiya, M. Morita, K. Morishita, Y. Sugimura and D. Yurgelun-Todd, Food and Nutrition Sciences, Vol. 3 No. 6, 2012, pp. 769-773. doi: 10.4236/fns.2012.36103.
- The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of citicoline on memory in healthy elderly with age-associated memory impairment.
- 100 healthy men and women participated in this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
- The subjects received a daily dose of either 500 mg citicoline or placebo for 12 weeks, and memory function was assessed at baseline and at the end of the intervention using computerized tests..
- Subjects using citicoline showed significantly greater improvements in memory performance, especially episodic memory.

Eri Nakazaki, Eunice Mah, Kristen Sanoshy, Danielle Citrolo, Fumiko Watanabe, The Journal of Nutrition, Volume 151, Issue 8, August 2021, Pages 2153–2160, https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxab119
Performance Breakdown:
- Improved cognition & reaction time ⬆
- Attenuated spikes in blood glucose caused by high stress response ⬇
- Increased subjective well-being ⬆
Mechanism of Action:
- Red Panax Ginseng is a plant root with a long history of traditional medicine containing high levels of ginsenosides. These exhibit a large variety of pharmacological effects including neuroprotection and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Read more about Red Panax Ginseng!
Annotated References:
- This study examined the effects of a single dose of Panax ginseng on cognitive performance in 30 healthy adult volunteers in a double-bline, placebo-controlled study..
- The subjects were givn either 200 mg or 400 mg of Panax ginseng, or a placebo.
- The subjects completed a 10 minute test battery at baseline, and then six times in immediate sucession starting 1 hour after supplementation.
- The tests inclused a Serial Threes suntraction task, a Serial Sevens task, a Rapid Visual Information Processing task, and a "mental fatigue" visual analogue scale. Blood glucose was also measured.
- Subjects given the 200 mg dose of Panaxi ginseng had the most significant improvements in the Serial Sevens subtraction task and reduction of subjective mental fatigue. Both doses of Panax ginseng resuced the subjects' blood glucose levels.

Reay JL, Kennedy DO, Scholey AB. J Psychopharmacol. 2005 Jul;19(4):357-65. doi: 10.1177/0269881105053286.
- The goal of this study was to examine relationship between elicit cognitive improvements and lower blood glucose levels caused by single doses of Panax ginseng.
- 27 healthy young adults were examined in this double-bline, placebo-controlled study. The subjects completed a 10 minute "cognitive demand" test battery at baseline, then consumed capsules containing either 200 mg Ginseng or placebo, and 30 minutes later consumed a drink containing either 25 g glucose or placebo. Another 30 mnutes later, the subjects completed the "cognitive demand" battery six times in immediate succession.
- The 10 minute “cognitive demand” battery comprised a Serial Threes subtraction task, a Serial Sevens subtraction task, a Rapid Visual Information Processing task, and a “mental fatigue” visual analogue scale. Blood glucose levels weree also measured before and after completions of the battery.
- The results showed that both Panax Ginseng and glucose were able to enhance the performance of mental erithmetic tasks and reduced the subjective feelings of fatigue during the sustained tests. There was no evidence of any synergistic relationship between Panax ginseng and exogenous glucose ingestion.

Reay JL, Kennedy DO, Scholey AB. J Psychopharmacol. 2006 Nov;20(6):771-81. doi: 10.1177/0269881106061516.
Performance Breakdown:
- Improved cognition ⬆
- Prevents cognitive decline ⬇
- Reduced symptoms of attention-decicit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) ⬇
Mechanism of Action:
- This nootropic compound is a fat-soluble amino acid derivative found in high amounts in the brain. Supplementation of phosphatidylserine contributes to the formation and maintenance of healthy cellular membranes.
Read more about Phosphatidylserine!
Annotated References:
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of a phosphatidylserine-containing formulation on cognitive function before and after intense resistence exercise.
- 18 trained college-aged males ingested 400 mg of soy-derived phosphatidylserine (PS) in a suplement called IQPLUS, or placebo for 14 days in a randomized, double-blined, placebo-controlled trial.
- After 14 days of supplementation, the subjects performed an acute bout of lower body resistance training. A cognitive function test in the form of Serial Subtraction Test (SST) was measured prior to exercise, 5 minutes after, and again 60 minutes after.
- The group supplementing with Phosphatidylserine had significant improvements in the cognitive function test before training, including a 20% reduction in time needed for a correct calculation, a 39% reduction in the total number of errors, and a 13% increase in the number of correct calculations.

Parker AG, Gordon J, Thornton A, Byars A, Lubker J, Bartlett M, Byrd M, Oliver J, Simbo S, Rasmussen C, Greenwood M, Kreider RB. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2011 Oct 21;8:16. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-8-16.
- This study examined the effects of phosphatidylserine supplementation on cognitive function of elderly Japanese subjects with memory complaints.
- 78 subjects were randomly assigned in this double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to take wither 100 mg or 300 mg Phosphatidylserine (PS) or placebo daily for 6 months.
- The subjects were tested before and after the 6-month trial by RBMT which is a standardized and validated test for memory functions, and by DWR where a sunject is presented with 3 unrelated words and is later asked to recall them.
- Subjects in the 100 mg phosphatidylserine group had the most significant improvements in the cognitive performance tests, especially those who were categorized in the low-score subgroup at the beginning of the trial.
- Subjects in the 100 mg phosphatidylserine group also showed memory improvments which were mostly attributed to the increase in delayed verbal recall, a memory ability attenuated in the earliest stages of dementia.

Kato-Kataoka A, Sakai M, Ebina R, Nonaka C, Asano T, Miyamori T. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010 Nov;47(3):246-55. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.10-62.
- This study investigated whether supplementation of phosphatidylserine, the naturally-occuring phospholipid, could improve ADHD symptoms in children.
- 36 children with symptoms of ADHD, but no prior drug treatment were given either 200 mg PS or placebo daily for 2 months in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled manner.
- Study measures included ADHD symptoms based on DSM-IV-TR, short-term auditory memory and working memory using the Digit Span Test of the Wechsler Intelligence Scal for Children, and mental performance to visual stimuli (GO/NO GO task).
- Phosphatidylserine supplementation had significant improvements in AHDH symptoms, short-term auditory memory, and inattention and impulsivity.

Hirayama S, Terasawa K, Rabeler R, Hirayama T, Inoue T, Tatsumi Y, Purpura M, Jäger R. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2014 Apr;27 Suppl 2:284-91. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12090.
Performance Breakdown:
- Increased cognition ⬆
- Prevents cognitive decline ⬇
- Increased attention and focus ⬆
Mechanism of Action:
- Huperzine A is a nootropic compound derived from the ancient chinese herb, Huperzia serrata, which promotes the expression of the learning neurotransmitter acetylcholine. It does this by inhibiting acetylcholine esterase, an enzyme which breaks down and degrades acetylcholine.
Annotated References:
- This comprehensive review underlines key research findings regarding Huperzine A supplementation ranging from biochemical mechanism of action, cellular and pharmacokinetic effects in model organisms, and phase IV clinical trials in humans.
- ANNOTATION.
- Compared with the common medications available to treat Alzheimer's diseases (tacrine, donepezil, and rivastigmine), HupA has better penetration through the blood-brain barrier, higher oral bioavailability, and longer duration of AChE inhibitory action.
- HupA has been found to improve cognitive deficits in a broad range of animal models including rodents and primates.
- Pharmacokinetic studies in rodents, canines, and healthy human volunteers indicated that HupA was absorbed rapidly, distributed widely in the body, and eliminated at a moderate rate with the property of slow and prolonged release after oral administration.
- Animal and clinical safety tests showed that HupA had no unexpected toxicity.
- The phase IV clinical trials in China have demonstrated that HupA significantly improved memory deficits in elderly people with benign senescent forgetfulness, and patients with Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia, with minimal peripheral cholinergic side effects and no unexpected toxicity.

Wang R, Yan H, Tang XC. Progress in studies of huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006 Jan;27(1):1-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00255.x.
- This study showed that Hup A not only promoted the proliferation of cultured mouse embryonic hippocampal neural stem cells (NSCs), but also increased the newly generated cells in the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the hippocampus in adult mice.
- Administration of Hup A to adult mice significantly enhanced the cell proliferation in dentate gyrus of hippocampus, and increased the remaining newborn cells 4 weeks after the drug administration.
- Newly generated BrdUþ/NeuNþ neurons were also increased by Hup A treatment.
- These findings suggest a novel role of Hup A in neurogenesis and provide a new insight into its therapeutic effects in neurological disorders via a neurogenesis-related mechanism.

Ma T, Gong K, Yan Y, Zhang L, Tang P, Zhang X, Gong Y. Brain Res. 2013 Apr 19;1506:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.02.026.
Performance Breakdown:
- Reduced fatigue under acute stress ⬇
- Increased cognition ⬆
- Increased subjective well-being ⬆
Mechanism of Action:
- Rhodiola rosea is a popular adaptogenic herb which has been used to help reduce fatigue under stressful situations.
Read more about Rhodiola Rosea!
Annotated References:
- This study examined the effects of a single dose of Rhodiola rosea extract on capacity for mental work against a background of fatigue and stress.
- 161 cadets aged 19 to 21 years old were used as subjects in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled manner.
- The subjects were given either 370 mg or 555 mg Rhodiola rosea, placebo, or no treatment for 5 days while performing regular military night duties.
- The study showed a pronounced antifatigue effect reflected in an antifatigue index, with no difference between the two doses of Rhodiola Rosea.

Shevtsov VA, Zholus BI, Shervarly VI, Vol'skij VB, Korovin YP, Khristich MP, Roslyakova NA, Wikman G. Phytomedicine. 2003 Mar;10(2-3):95-105. doi: 10.1078/094471103321659780.
- This study aimed to explore the clinical outcomes in burnout patients treated with Rhodiola rosea in an exploratory, noncontrolled manner.
- 118 patients experiencing burnout were given a 400 mg dose of Rhodiola rosea daily for 12 weeks and tested for a wide range of rating scales to provide a basis for the planning of sunsequent studies.
- Clinical assessments included the Maslach Burnout Inventory, Burnout Screening Scales I and II, Sheehan Disability Scale, Perceived Stress Questionnaire, Number Connection Test, Multidimensional Mood State Questionnaire, Numerical Analogue Scales for different stress symptoms and impairment of sexual life, Patient Sexual Function Questionnaire, and the Clinical Global Impression Scales.
- The results showed a clear improvement across the board over time with Rhodiola rosea supplementation. The most significant improvements were seen within the first week of supplementation.

Kasper S, Dienel A. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017 Mar 22;13:889-898. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S120113.
- This study examined the effects of 400 mg Rhodiola rosea supplementation in 100 subjects with prolonged or chronic fatigue symptoms in an uncontrolled, open-label multicenter clinical trial.
- The subjects were administered 2 x 200 mg Rhodiola rosea daily for 8 weeks.
- Outcome measures were scales and tests related to fatigue.
- The results showed significant improvement in all all the fatigue indexes over the 8 week trial, with the most significant improvement after one week.

Lekomtseva Y, Zhukova I, Wacker A. Complement Med Res. 2017;24(1):46-52. doi: 10.1159/000457918.
- The aim of this study was to examine the effect of acute Rhodiola rosea ingestion on substrate utilisation, mood state, RPE, and exercise affect in a random, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
- Subjects were 10 active males given either 3 mg/kg Rhodiola rosea (210 mg for 150 lbs person) or placebo before completing two 30-minute cycling trials and an intensity of 70% VO2 max.
- Subjects were tested for mood state and exercise affect before, during, and after exercise.
- The results show that Rhodiola rosea was effective in significantly reducing the rating of perceived exertion over time during exercise, and also significantly improved the feeling of pleasure after exercise.

Duncan MJ, Clarke ND. J Sports Med (Hindawi Publ Corp). 2014;2014:563043. doi: 10.1155/2014/563043.
Performance Breakdown:
- Increased memory & working memory ⬆
- Increased attention ⬆
- Increased cognitive processing efficiency ⬆
Mechanism of Action:
- Bacopa monnieri is a nootropic herb which has been used in traditional medicine for longevity and cognitive enhancement. Based on the available research, bacopa may work by decreasing levels of acetylcholine esterase, an inhibitor of the learning neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Read more about Bacopa Monnieri!
Annotated References:
- The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Bacopa monnieri on cognitive function an affect, and its safety and tolerability in 54 healthy elderly study participants.
- 48 participants completed this randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with a 6-week placebo run-in period followed by 12 weeks of treatment with 300 mg Bacopa monnieri daily or placebo.
- Measured outcomes included the delayed recall score from the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (AVLT), the Stroop Task assessing the ability to ignore irrelevant information, the Divided Attention Task (DAT), the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) letter-digit test of immediate working memory State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression scale (CESD)-10 depression scale, and the Profile of Mood States.
- Bacopa participants had enhanced AVLT delayed word recall memory scores relative to placebo, and the Bacopa group improved on the Stroop task, although the changes were insignificant. CESD-10 depression scores, combined state plus trait anxiety scores, and heart rate decreased over time for the Bacopa group but increased for the placebo group.
- Bacopa participants reported no negative side-effects, and the dose of 300 mg was well tolerated.

Calabrese C, Gregory WL, Leo M, Kraemer D, Bone K, Oken B. J Altern Complement Med. 2008 Jul;14(6):707-13. doi: 10.1089/acm.2008.0018.
- This study aimed to determine the effect of B. monnieri on attention, cognitive processing, working memory, and cholinergic and monoaminergic functions in healthy elderly.
- A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled design was utilized on 60 healthy elderly subjects receiving either 300 mg or 600 mg Bacopa monnieri or a placebo once daily for 12 weeks.
- The cholinergic and monoaminergic systems functions were determined using AChE and MAO activities. Working memory was assessed using percent accuracy and reaction time of various memory tests as indices, whereas attention and cognitive processing were assessed using latencies and amplitude of N100 and P300 components of event-related potential. All assessments were performed before treatment, every four weeks throughout study period, and at four weeks after the study.
- The results show Bacopa monnieri treatment improved working memory and decreased latencies, while suppressing the Acetylcholine Esterase activity.

Peth-Nui T, Wattanathorn J, Muchimapura S, Tong-Un T, Piyavhatkul N, Rangseekajee P, Ingkaninan K, Vittaya-Areekul S. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:606424. doi: 10.1155/2012/606424.
Performance Breakdown:
- Prevents cognitive decline ⬇
- Increased memory recall ⬆
- Increased processing speed & accuracy ⬆
- Reduced symptoms associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) ⬇
Mechanism of Action:
- Ginkgo Biloba is the most commonly ingested herb for brain health and support. This nootropic plant compound is most commonly used to prevent the natural process of cognitive decline.
Read more about Ginkgo Biloba!
Annotated References:
- This study aimed to assess the efficacy of a 240 mg once-daily preparation of Ginkgo biloba extract in 404 outpatients ≥ 50 years old diagnosed with mild to moderate dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, or vascular dementia.
- Ginkgo biloba (EGb 761®) improved cognitive functioning, neuropsychiatric symptoms and functional abilities in both types of dementia.

Ihl R, Tribanek M, Bachinskaya N; GOTADAY Study Group. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2012 Mar;45(2):41-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1291217.
- This study employed a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, 24-week trial with 410 outpatients to demonstrate efficacy and safety of a 240 mg once-daily formulation of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in patients with mild to moderate dementia associated with neuropsychiatric symptoms.
- Primary outcomes were the changes from baseline to week 24 in the SKT and NPI total scores.
- The ADCS Clinical Global Impression of Change (ADCS-CGIC), Verbal Fluency Test, Activities of Daily Living International Scale (ADL-IS), DEMQOL-Proxy quality-of-life scale and 11-point box scales for tinnitus and dizziness were secondary outcome measures.
- Patients supplementing with Ginkgo biloba showed improvements clinically relevant improvement in cognition, psychopathology, functional measures, and quality of life.

• Herrschaft H, Nacu A, Likhachev S, Sholomov I, Hoerr R, Schlaefke S. J Psychiatr Res. 2012 Jun;46(6):716-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.03.003.
- The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of EGb 761 on memory and the specificity of such effects on distinct memory functions in middle-aged healthy volunteers.
- A total of 188 healthy subjects aged 45–56 years were randomised to receive EGb 761 (240 mg once daily) or placebo for 6 weeks.
- Outcome measures were the change in memory performance in a demanding standardised free recall paradigm and a less demanding standardised recognition test.
- EGb 761-treated subjects improved significantly in quantity of recall. Other test improvements were statistically insignificant.

Kaschel R. Phytomedicine. 2011 Nov 15;18(14):1202-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2011.06.021.
- This study examined whether Ginkgo biloba would be beneficial for treatment of ADHD by using a double blind, randomized, parallel group comparison of Ginkgo biloba and methylphenidate (ritalin).
- Fifty outpatients (39 boys and 11 girls) with a DSM-IV-TR diagnosis of ADHD were study population of this trial.
- The subjects were treated with 80-120 mg Ginkgo biloba daily for 6 weeks, or 20-30 mg of methylphenidate for comparison. Doses ranged based on the patients' weights.
- The principal measure of outcome was the Teacher and Parent ADHD Rating Scale- IV. Asessments were done at baseline and at 21 and 42 days after the medication started.
- Treatment with Ginkgo biloba was associated with reduced symptoms of ADHD as assessed by parental and teacher assessment, although the effects were significantly lesser than the reference drug methylphenidate.

Salehi B, Imani R, Mohammadi MR, Fallah J, Mohammadi M, Ghanizadeh A, Tasviechi AA, Vossoughi A, Rezazadeh SA, Akhondzadeh S. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Feb 1;34(1):76-80. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.09.026.